glPixelStore
NAME
glPixelStoref, glPixelStorei -- set pixel storage modes
C SPECIFICATION
void glPixelStoref(GLenum pname,
GLfloat param)
void glPixelStorei(GLenum pname,
GLint param)
PARAMETERS
- pname
-
Specifies the symbolic name of the parameter to be set. Six values
affect the packing of pixel data into memory:
GL_PACK_SWAP_BYTES, GL_PACK_LSB_FIRST,
GL_PACK_ROW_LENGTH, GL_PACK_SKIP_PIXELS,
GL_PACK_SKIP_ROWS, and GL_PACK_ALIGNMENT.
Six more affect the unpacking of pixel data from memory:
GL_UNPACK_SWAP_BYTES, GL_UNPACK_LSB_FIRST,
GL_UNPACK_ROW_LENGTH, GL_UNPACK_SKIP_PIXELS,
GL_UNPACK_SKIP_ROWS, and GL_UNPACK_ALIGNMENT.
- param
-
Specifies the value that pname is set to.
DESCRIPTION
glPixelStore sets pixel storage modes that affect the operation of
subsequent
glDrawPixels and
glReadPixels
as well as the unpacking of polygon stipple patterns (see
glPolygonStipple),
bitmaps (see
glBitmap),
and texture patterns (see
glTexImage1D, and
glTexImage2D).
pname is a symbolic constant indicating the parameter to be set, and
param is the new value. Six of the twelve storage parameters affect
how pixel data is returned to client memory, and are therefore significant
only for
glReadPixels or
glGetTexImage
commands. They are as follows:
- GL_PACK_SWAP_BYTES
-
If true, byte ordering for multibyte color components, depth
components, color indices, or stencil indices is reversed. That is,
if a four-byte component is made up of bytes b0, b1,
b2, b3, it is stored in memory as b3, b2,
b1, b0 if GL_PACK_SWAP_BYTES is true.
GL_PACK_SWAP_BYTES has no effect on the memory order of
components within a pixel, only on the order of bytes within
components or indices. For example, the three components of a
GL_RGB format pixel are always stored with red first,
green second, and blue third, regardless of the value of
GL_PACK_SWAP_BYTES.
- GL_PACK_LSB_FIRST
-
If true, bits are ordered within a byte from least significant
to most significant; otherwise, the first bit in each byte is the
most significant one. This parameter is significant for bitmap
data only.
- GL_PACK_ROW_LENGTH
-
If greater than zero, GL_PACK_ROW_LENGTH defines the number of
pixels in a row. If the first pixel of a row is placed at location
p in memory, then the location of the first pixel of the next
row is obtained by skipping
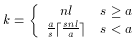
components or indices, where n is the number of components or
indices in a pixel, l is the number of pixels in a row
(GL_PACK_ROW_LENGTH if it is greater than zero, the width
argument to the pixel routine otherwise), a is the value of
GL_PACK_ALIGNMENT, and s is the size, in bytes, of a
single component (if a < s, then it is as if a = s). In the case
of 1-bit values, the location of the next row is obtained by skipping
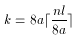
components or indices.
The word component in this description refers to the nonindex
values red, green, blue, alpha, and depth. Storage format
GL_RGB, for example, has three components per pixel: first red,
then green, and finally blue.
- GL_PACK_SKIP_PIXELS and GL_PACK_SKIP_ROWS
-
These values are provided as a convenience to the programmer;
they provide no functionality that cannot be duplicated simply
by incrementing the pointer passed to
glReadPixels.
Setting GL_PACK_SKIP_PIXELS to i is equivalent to
incrementing the pointer by i*n components or indices,
where n is the number of components or indices in each pixel.
Setting GL_PACK_SKIP_ROWS to j is equivalent to
incrementing the pointer by j*k components or indices,
where k is the number of components or indices per row, as
computed above in the GL_PACK_ROW_LENGTH section.
- GL_PACK_ALIGNMENT
-
Specifies the alignment requirements for the start of each pixel row
in memory. The allowable values are 1 (byte-alignment), 2 (rows
aligned to even-numbered bytes), 4 (word alignment), and 8
(rows start on double-word boundaries).
The other six of these twelve storage parameters affect how pixel data is
read from client memory. These values are significant for
glDrawPixels,
glTexImage1D,
glTexImage2D,
glBitmap, and
glPolygonStipple.
They are as follows:
- GL_UNPACK_SWAP_BYTES
-
If true, byte ordering for multibyte color components, depth
components, color indices, or stencil indices is reversed. That is,
if a four-byte component is made up of bytes b0, b1,
b2, b3, it is taken from memory as b3, b2,
b1, b0 if GL_UNPACK_SWAP_BYTES is true.
GL_UNPACK_SWAP_BYTES has no effect on the memory order of
components within a pixel, only on the order of bytes within
components or indices. For example, the three components of a
GL_RGB format pixel are always stored with red first, green
second, and blue third, regardless of the value of
GL_UNPACK_SWAP_BYTES.
- GL_UNPACK_LSB_FIRST
-
If true, bits are ordered within a byte from least significant
to most significant; otherwise, the first bit in each byte is the
most significant one. This parameter is significant for bitmap
data only.
- GL_UNPACK_ROW_LENGTH
-
If greater than zero, GL_UNPACK_ROW_LENGTH defines the number of
pixels in a row. If the first pixel of a row is placed at location
p in memory, then the location of the first pixel of the next
row is obtained by skipping
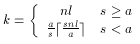
components or indices, where n is the number of components or
indices in a pixel, l is the number of pixels in a row
(GL_UNPACK_ROW_LENGTH if it is greater than zero, the width
argument to the pixel routine otherwise), a is the value of
GL_UNPACK_ALIGNMENT, and s is the size, in bytes, of a
single component (if a < s, then it is as if a = s). In the case
of 1-bit values, the location of the next row is obtained by skipping
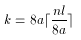
components or indices.
The word component in this description refers to the nonindex
values red, green, blue, alpha, and depth. Storage format
GL_RGB, for example, has three components per pixel: first red,
then green, and finally blue.
- GL_PACK_SKIP_PIXELS and GL_PACK_SKIP_ROWS
-
These values are provided as a convenience to the programmer;
they provide no functionality that cannot be duplicated simply
by incrementing the pointer passed to
glDrawPixels,
glTexImage1D,
glTexImage2D,
glBitmap, or
glPolygonStipple.
Setting GL_UNPACK_SKIP_PIXELS to i is equivalent to
incrementing the pointer by i*n components or indices,
where n is the number of components or indices in each pixel.
Setting GL_UNPACK_SKIP_ROWS to j is equivalent to
incrementing the pointer by j*k components or indices,
where k is the number of components or indices per row, as
computed above in the GL_UNPACK_ROW_LENGTH section.
- GL_UNPACK_ALIGNMENT
-
Specifies the alignment requirements for the start of each pixel row
in memory. The allowable values are 1 (byte-alignment), 2 (rows
aligned to even-numbered bytes), 4 (word alignment), and 8
(rows start on double-word boundaries).
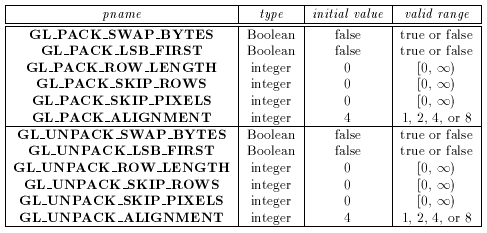
The following table gives the type, initial value, and range of valid
values for each of the storage parameters that can be set with
glPixelStore.
glPixelStoref can be used to set any pixel store parameter. If the
parameter type is Boolean, then if param is 0.0, the parameter is false;
otherwise it is set to true. If pname is a integer type parameter,
param is rounded to the nearest integer.
Likewise, glPixelStorei can also be used to set any of the pixel store
parameters. Boolean parameters are set to false if param is 0 and true
otherwise. param is converted to floating point before being assigned to
real-valued parameters.
NOTES
The pixel storage modes in effect when
glDrawPixels,
glReadPixels,
glTexImage1D,
glTexImage2D,
glBitmap, or
glPolygonStipple
is placed in a display list control the interpretation of memory data.
The pixel storage modes in effect when a display list is executed are not
significant.
ERRORS
GL_INVALID_ENUM is generated if pname is not an accepted value.
GL_INVALID_VALUE is generated if a negative row length, pixel skip,
or row skip value is specified, or if alignment is specified other than
1, 2, 4, or 8.
GL_INVALID_OPERATION is generated if glPixelStore is called
between a call to glBegin and the
corresponding call to glEnd.
ASSOCIATED GETS
glGet with argument
GL_PACK_SWAP_BYTES
glGet with argument
GL_PACK_LSB_FIRST
glGet with argument
GL_PACK_ROW_LENGTH
glGet with argument
GL_PACK_SKIP_ROWS
glGet with argument
GL_PACK_SKIP_PIXELS
glGet with argument
GL_PACK_ALIGNMENT
glGet with argument
GL_UNPACK_SWAP_BYTES
glGet with argument
GL_UNPACK_LSB_FIRST
glGet with argument
GL_UNPACK_ROW_LENGTH
glGet with argument
GL_UNPACK_SKIP_ROWS
glGet with argument
GL_UNPACK_SKIP_PIXELS
glGet with argument
GL_UNPACK_ALIGNMENT
SEE ALSO
glBitmap,
glDrawPixels,
glPixelMap,
glPixelTransfer,
glPixelZoom,
glPolygonStipple,
glReadPixels,
glTexImage1D,
glTexImage2D
back to the OpenGL index page
© 1995 Uwe Behrens. All rights reserved.